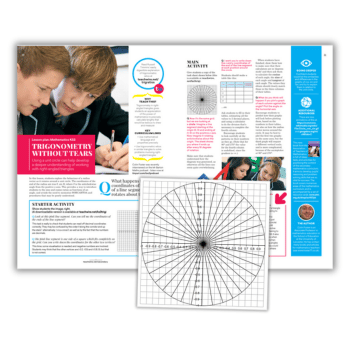
Using a unit circle can help develop a deeper understanding of trigonometry in right-angled triangles.
In this maths lesson, students explore the behaviour of a radius vector as it rotates around a unit circle.
The coordinates of the end of the radius are (cos θ, sin θ), where θ is the anticlockwise angle from the positive x-axis.
This provides a way to introduce students to the sine and cosine ratios as functions of an angle. It also avoids the need to memorise SOHCAHTOA and procedures that students may not understand well.
Why teach this?
Trigonometry in right-angled triangles gives students an appreciation of the power of mathematics to precisely calculate lengths that would be tedious to draw and measure.
Key curriculum links
- Use mathematical language and properties precisely
- Use trigonometric ratios in similar triangles to solve problems involving right-angled triangles
Starter activity
Show students the included image. Look at this pink line segment. Can students tell you the coordinates of the ends of the line segment?
This task is really to check that students can read off decimal coordinates correctly. They may be confused by the order (“along the corridor and up the stairs”; alternatively, “x is a-cross”), as well as by the fact that the numbers are decimals.
The pink line segment is one side of a square which fits completely on the grid. Can students write down the coordinates for the other two vertices?
This time, some visualisation is needed, and negative numbers are involved. Students may think that the other vertices are (-0.2, -0.5) and (-0.8, 0), but that is not correct.
Colin Foster is an associate professor in mathematics education at the School of Education at the University of Leicester. He has written many books and articles for mathematics teachers.