This KS3 maths trigonometry lesson introduces sin, cos and tan, with a little quiz and questions at the the end.
KS3 maths trigonometry introduction
We use trigonometry to find missing angles and lengths of triangles. Trigonometry uses three functions. These are called:
- Sine (shortened to ‘sin’ and pronounced ‘sign’)
- Cosine (shortened to ‘cos’)
- Tangent (shortened to ‘tan’)
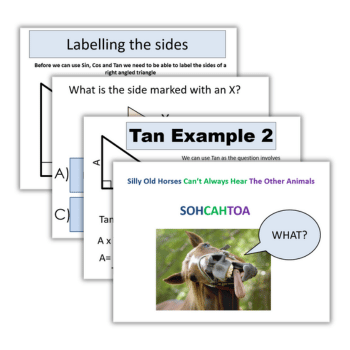
Before they can use sin, cos and tan, pupils need to be able to label the sides of a right-angled triangle. The longest side, the one opposite the right angle, is called the hypotenuse.
What you call the other two sides changes depending on which angle you’re working with. This resource contains ten multiple choice questions about labelling right-angled triangles for students to have a go at.
- We use sine when we have the opposite length and the hypotenuse
- We use cosine when we have the adjacent length and the hypotenuse
- We use tangent when we have the opposite and adjacent lengths
Curriculum area
Geometry and measures Use Pythagoras’ Theorem and trigonometric ratios in similar triangles to solve problems involving right-angled triangles
Ben Cooper is a maths teacher in Birmingham. You can find more of his resources on his TES Page bcooper87, and follow him on Twitter at @bcoops_online. Browse more Key Stage 3 maths worksheets.